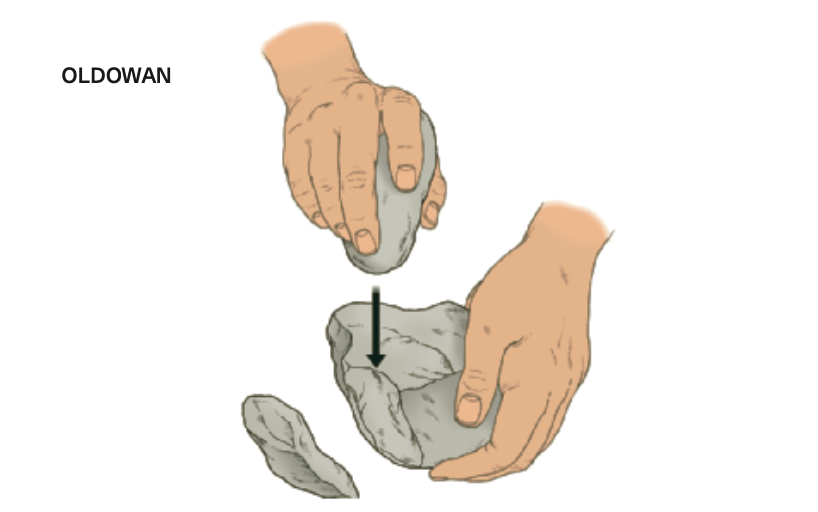
Recent class discussions have consisted of explaining the importance and impact of lithics on archeological discoveries. The term lithic is derived from ancient Greek and means rock. This is why lithic technology can be defined as certain techniques that are used to produce various categories of stone tools. The first stone tools from two and a half million years before the present can be characterized as simplistic and non-selective. However, as time progressed significant additions were made to lithics further enhancing hominins’ ability to manipulate these stone tools to their benefit. Early lithics are smaller sections of stone that were produced by striking two stones together. This type of lithic is uniface, meaning that only one side of the stone had been flaked. Whereas the lithics that are more recent are biface tools meaning that two sides have been flaked. The resulting tool has a distinct purpose for each side. In addition, lithics began to be produced with stones of higher quality and structure leading to stronger tools. Furthermore, lithics began to become more symmetrical which shows that hominins underwent adaptations progressively. As time continued to progress lithic technology became even more advanced resulting in different facets of stone stools. Stone tools morphed from uncomplicated scrapers to intricate arrowheads. As hominins progressed, the tools that they used became more complex to keep up with their more elaborate lifestyle. Determining factors of more recent lithics are the bulb point near the bottom of the stone. The bulb point was formed as a result of a stone being struck against another hard surface. These identifiers are crucial in determining the period in which a certain lithic was used. Lastly, these devices molded human advancement and contributed to the development of hominins.
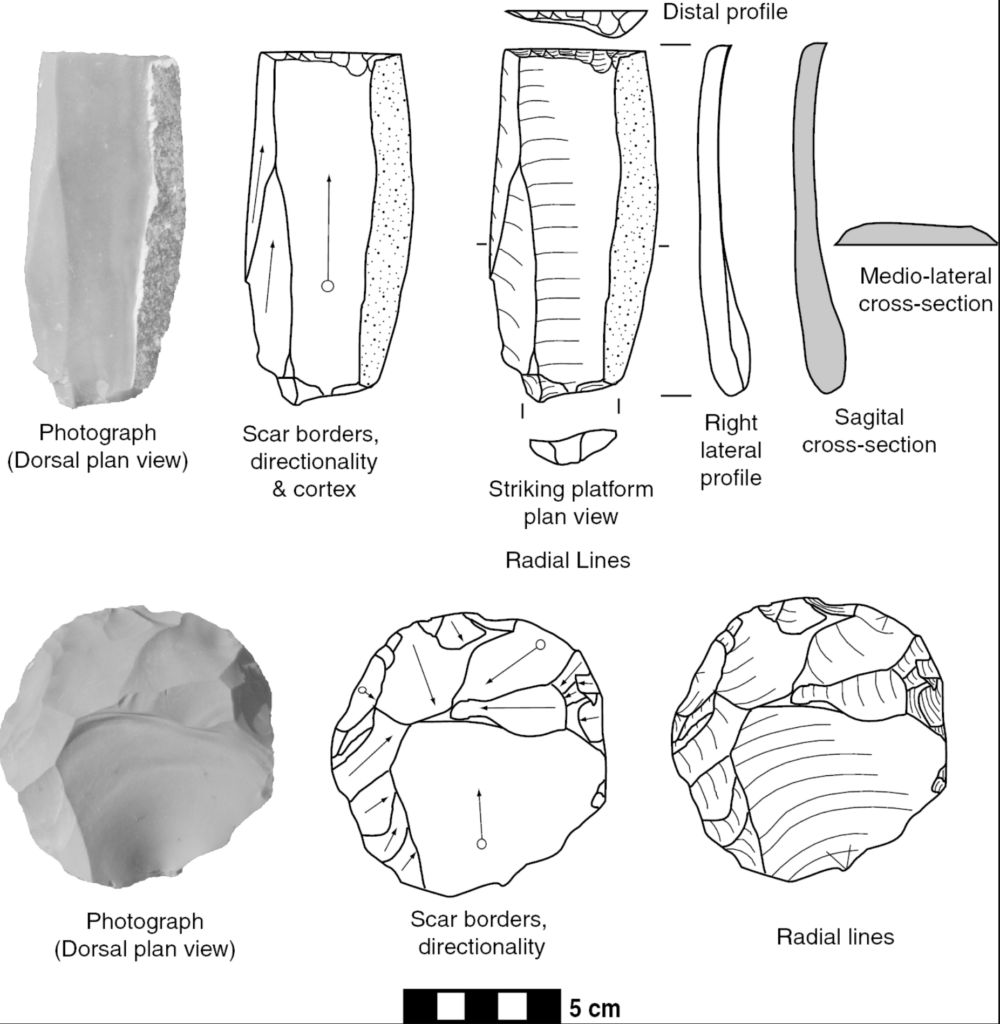
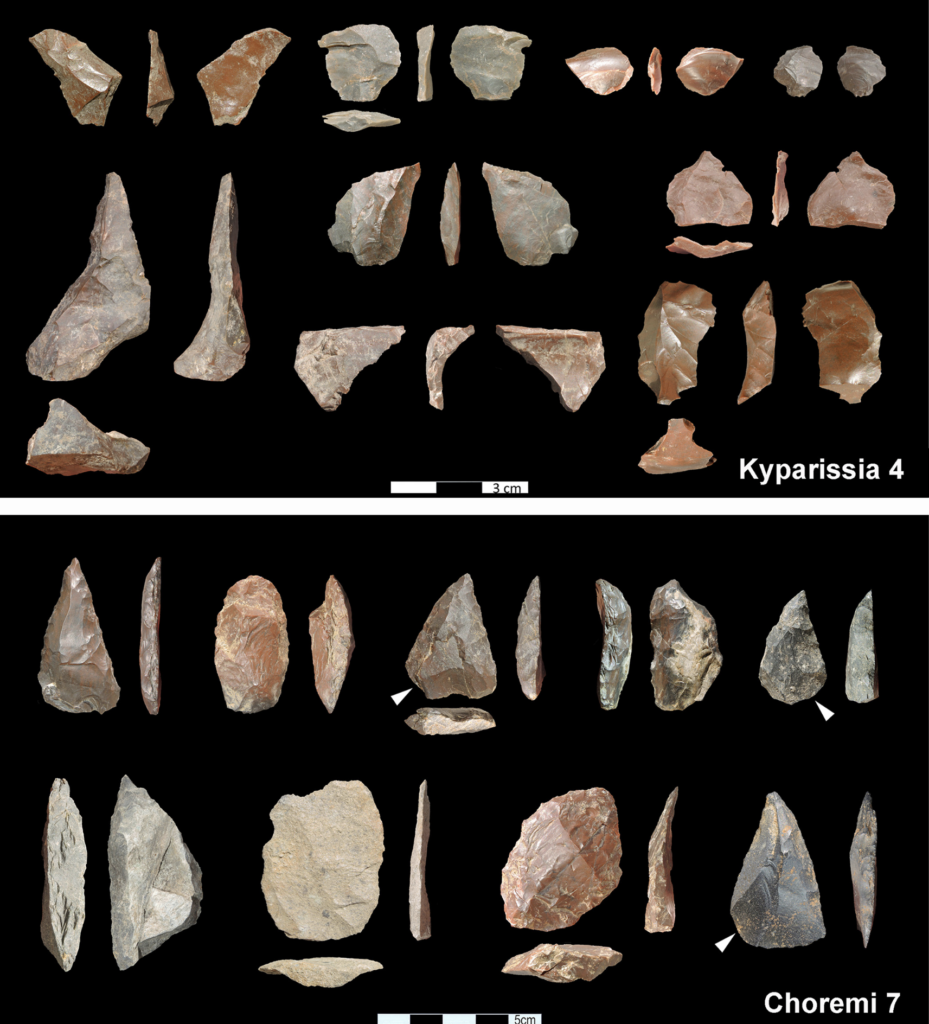
Lithics are being discovered all throughout the world. Recently expert archaeologists: Panagiotis Karkanas, Eleni Panagopoulou, and Katerina Harvati found lithics that are from a “quarter of a million years before present.”(Paphitis 2023) The artifacts were unearthed from a site in the infamous “Megalopolis region of modern Greece.”(Paphitis 2023) These scientists reported that “rough stone tools”(Paphitis 2023) were observed at the site. Since these artifacts were simple stone tools that had sharp flakes it uncovers that they are from the “Lower Paleolithic stone tool industry.”(Paphitis 2023) The tools’ distinct shape and clear edges prove that the tools’ main purpose was for slaughtering and preparation of meals. Also, these tools aided the cultivation process of other plant and animal matter for hominin consumption.

References:
Paphitis, Nicholas. “Newly discovered stone tools drag dawn of Greek archaeology back by a
quarter-million years.” ABC News. Last modified June 1, 2023. Accessed October 1, 2023.
https://abcnews.go.com/International/wireStory/newly-discovered-stone-tools-drag-dawn-greek-archaeology-99767958.
Shea, John J. “Lithics Basics.” Cambridge University Press & Assessment. Last modified March 5,
2013. Accessed October 1, 2023. https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/
stone-tools-in-the-paleolithic-and-neolithic-near-east/lithics-basics/
487AB7381E1E3B42C4980448AF364C40.
“Newly discovered stone tools drag dawn of Greek archaeology back by a quarter-million years.”
American School of Classical Studies at Athens. Last modified June 2, 2023. Accessed October 1,2023. https://ascsa.edu.gr/news/newsDetails/newly-discovered-stone-tools.
Further Readings: