
This is a reconstruction of Homo naledi built following 700 hours of work by paleoartist John Gurche.
On Thursday September 10, 2015 a group of scientists excavating a cave system in South Africa released their findings claiming that they may have made an important discovery about human evolution. In late 2013 and early 2014 the scientists discovered fifteen nearly-complete skeletons in a nearly-inaccessible chamber, now called the Dinaledi Chamber, and are now classifying them as a new species of hominin called the Homo naledi. The species warranted classification in the homo genus because of surprising human-like features, such as teeth and skull features similar to other members of the genus, and hand shapes that suggested tool-using capabilities. It also appears to be one of the genus’s most primitive members because it possesses a much smaller brain, shoulders shaped like those of apes, and extremely curved fingers demonstrating climbing capabilities.
The most significant finding of the expedition was that Homo naledi may have practiced a form of behavior previously thought to be unique only to humans. The isolation of the chamber and presence of few other animal bones led the team of scientists to believe that the bodies had been intentionally left there, perhaps as a burial ritual. The deposition of bodies in the same location is generally a cultural practice, and it appears that burials were repeatedly carried out in that specific location over the course of many years. The location was so incredibly isolated that when the team first discovered the chamber, bones lied directly on the surface, as they had not been affected by erosion, scavengers, or other climate conditions.
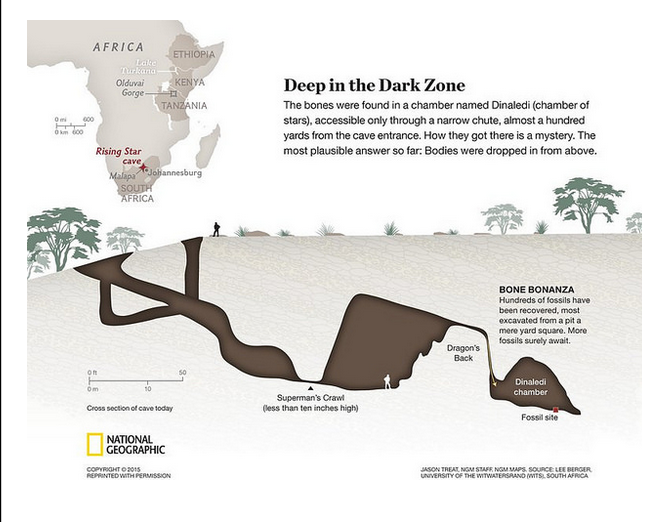
This is a map of the archaeological site, showing the complexity of the cave system and location of the fossil site.
The isolation of the archaeological site posed significant challenges for the team of researchers. The first expedition lasted 21 days during November 2013 and consisted of tedious extraction of the bones by carefully using toothpicks and brushes to gently remove the fossils and transport them up to the surface through a 7.5-inch chute. Sixty cavers and scientists were working on the excavation site, which also trained six women to be “underground astronauts” to fit through the narrow 18-centimeter cave opening. The depth of the cave made full excavation impractical, so the scientists were forced to finish removing the bones during a week-long expedition in early 2014.
Exploration of human origins has made significant strides as more remains of ancestors are being found. However there had been a million-year-long gap in the fossil record in which lies the beginning of mankind. The origin of the homo genus has been shrouded in mystery, but this discovery may help to fill in the pieces of the puzzle and uncover the true origin of mankind.
Sources:
http://popular-archaeology.com/issue/fall-2015/article/scientists-discover-new-early-human-species (images are also from this site)
http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-34192447
Further Reading:
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/09/150910084610.htm
http://elifesciences.org/content/4/e09560 (detailed published study report)
The NOVA/National Geographic Special, “Dawn of Humanity,” premieres September 16, 2015, at 9 p.m. ET/8 p.m. CT on PBS in the United States and is streaming online now at: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/dawn-of-humanity.html

This discovery is so important to archaeologists’ efforts to fill in the gaps of history about the early origins of humans. The Homo Naledi species poses new questions about the biological and cultural development of our primitive ancestors. We can explore the notion that the oldest humans buried their dead, and despite reduced brain size and ape-like traits, exhibited a degree of critical thinking and essentially, humanity. Other than the practicality and natural aversion to decomposing bodies, I wonder if the bones were deposited in the cave for spiritual reasons?
This is truly a great find for the skeletal information alone. The next step is to understand what culture revolved around this species and their bone chamber. If these were tool users and if this was a cultural deposit then there should be tools or other artifacts somewhere in the cave.
Professor, it is really interesting that you bring up this group’s potential use of tools, because within the past month, scientists have found bone evidence to further support their hypothesis that Homo naledi used tools. The hand and wrist bone samples indicate powerful holding and grasping abilities, and certain foot structures suggest that it even walked upright. The surprising lack of tools or fragments at the site also further supports that the bodies may have been deposited there as a burial practice. It is an interesting theory that hopefully will be further investigated in months to come.
http://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/newly-identified-human-ancestor-homo-naledi-was-handy-tools-n439656